
Best 10 3D Printers In India - 2025 Edition
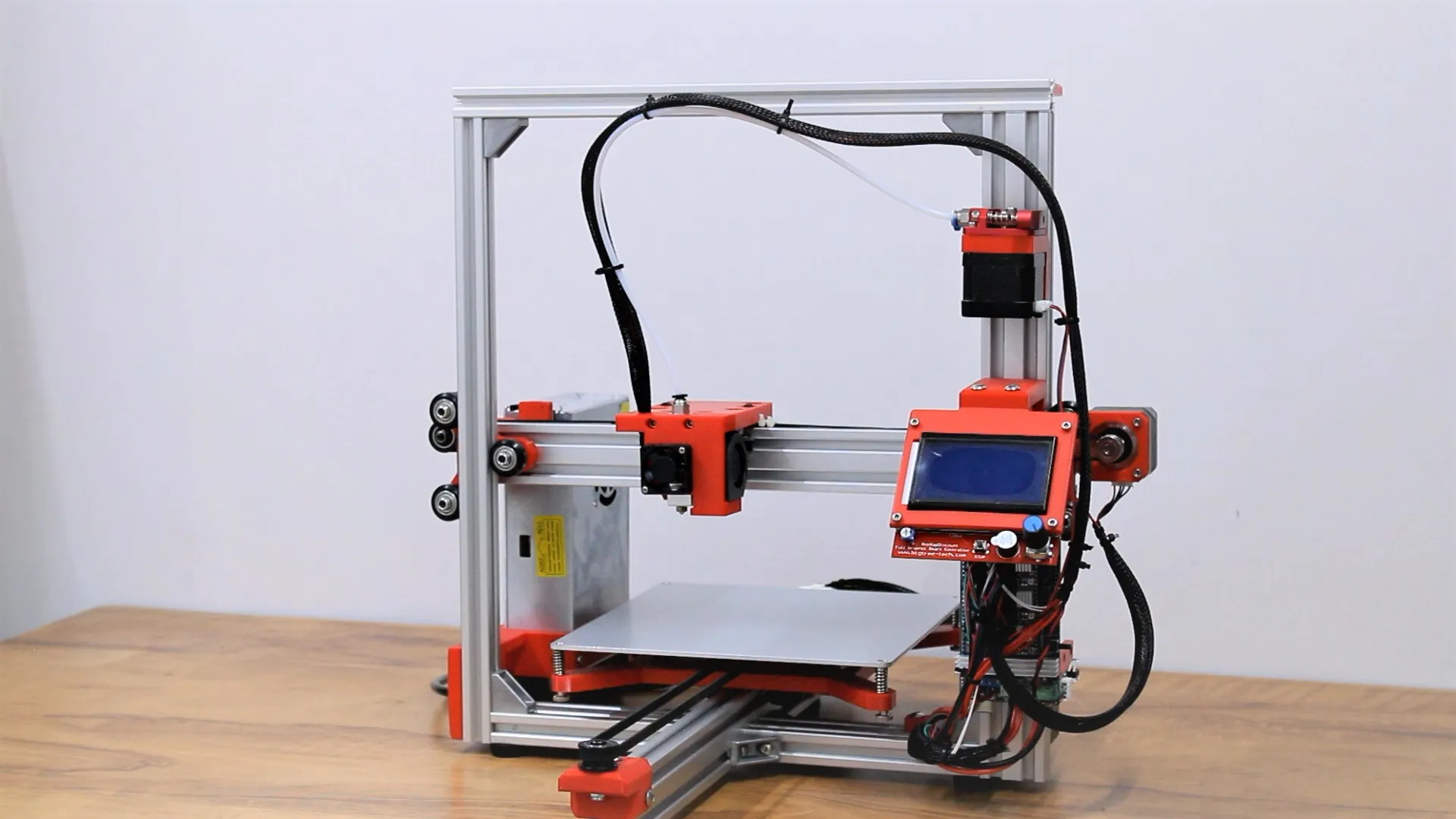
Selecting the ideal 3D printer involves considering several factors, including your budget and preferred printing needs. Various models offer different levels of control over the printing process and the final output quality.
While some printers are designed for high-resolution detail, others excel at speed or large-scale prints. There are also advanced models that can operate autonomously, requiring minimal manual intervention.
Types of 3D Printers: A Complete Overview
When exploring 3D printers, they primarily fall into two broad categories—FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) and resin-based printers. Within these, you’ll find subtypes based on material compatibility, resolution, speed, and use case: hobbyist, prosumer, industrial, and educational printers.
FDM 3D Printers
FDM printers are the most common and ideal for general-purpose printing. They work by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament in layers. Known for being budget-friendly and easy to use, they’re popular for home use, schools, and rapid prototyping.
Pros:
Affordable and widely available
Easy setup and maintenance
Compatible with many filament types
Great for functional models and quick prints
Cons:
Lower detail and surface quality
Visible layer lines
May require calibration and post-processing
Resin 3D Printers (SLA, DLP, LCD)
Resin printers use liquid photopolymer cured by light for high-detail prints. They’re perfect for intricate models like miniatures, dental molds, and jewelry, though they demand more post-processing and safety precautions.
Pros:
Exceptional print resolution and detail
Smooth surface finish
Ideal for precision work
Cons:
Resin can be messy and requires handling care
More post-processing steps
Higher ongoing material costs
Hobbyist 3D Printers
Designed for casual users, these printers focus on affordability and ease of use. Many come semi-assembled and include safety features and beginner-friendly software.
Pros:
Low entry cost
Simple controls and guided setup
Strong community support and upgrades
Cons:
Limited features and slower speeds
Smaller build volume
Prosumer 3D Printers
For serious enthusiasts and small businesses, these offer better hardware, higher speeds, and more precision. They often support advanced filaments and more customization.
Pros:
Greater accuracy and reliability
Support for advanced materials
Larger build volumes
Cons:
Higher price point
Requires more technical knowledge
Industrial 3D Printers
Used in manufacturing, these machines are built for performance, speed, and reliability. They can print large parts using advanced materials like nylon, carbon fiber, or metal composites.
Pros:
High throughput and repeatability
Excellent mechanical strength
Customizable for large-scale production
Cons:
Expensive and large footprint
Requires skilled operation and maintenance
Educational 3D Printers
These are optimized for classroom use with safety features, intuitive software, and reliability. They often include curriculum support for STEM learning.
Pros:
Safe and enclosed design
Easy-to-use interfaces
Built-in lesson plans or education tools
Cons:
Limited to basic printing needs
Smaller build sizes
Additional Features to Consider
When shopping for a 3D printer, keep these features in mind:
Build Volume: Larger prints require more space; choose a machine that fits your typical project size.
Print Speed: Faster printers save time but may reduce quality—balance both based on your needs.
Auto-Leveling Bed: Ensures consistent prints with minimal manual setup.
Material Compatibility: Some printers support a wide range of filaments or resins, while others are limited.
Connectivity: Look for USB, Wi-Fi, or SD card options for flexibility in file transfers.
Enclosed Chamber: Helps with temperature regulation and safety, especially for ABS and other sensitive filaments.
Final Thoughts
3D printers come in various types, each suited to different users and purposes. If you’re after creative control and hands-on learning, an FDM hobbyist printer may be ideal. If you’re focused on detail and quality, resin printers deliver unmatched results.
Ultimately, the best 3D printer for you depends on your experience level, project type, material preference, and budget. Choose a model that aligns with your goals, and you’ll be ready to bring your designs to life.
topreviewhome.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.in.
© topreviewhome.com 2025 | All Rights Reserved.









